Today is World Backup Day. A day to remind people to make copies of important data and back them up using various backup methods. The goal of a backup is well known. However, a simple copy is not enough to restore server data in the event of phishing, a power failure or a hardware defect: A good backup strategy is required. In this blog post, you will find out which backup types and methods you can use to secure your data and what a grandfather has to do with your backup strategy.

Before you start backing up data, you should define who is responsible for the data backup. They will deal with the question of which data should be backed up. To do this, it is advisable to get an overview of all directories. The directories that contain relevant data are then noted and suitable backup cycles are defined. Should data be backed up after the close of business or after every file change? And should a backup be carried out daily, weekly or monthly? The fact is: the more important the data, the more important regular backups are. Various examples and backup types will provide orientation.
Once all the data has been classified, it's time for the next step: What options are there for backing up the classified data? – Let's find out:
Full, differential or incremental! Depending on the type of backup, a backup takes up more or less storage space and is slower or faster when backing up or restoring data. We shed some light on the subject and take a closer look at the three backup types:
A full backup compiles every single file on a system into one backup file. As the entire file system of a server is backed up, this type of backup takes a long time to create. It is therefore important to choose a suitable time for the backup, e.g. at the end of the day or on a Sunday.
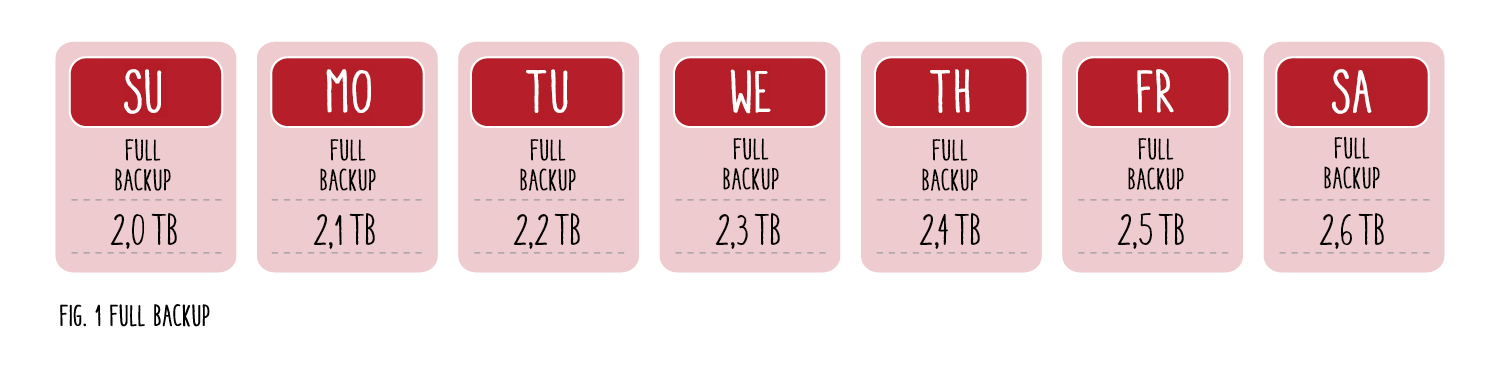
Suppose you make a daily backup copy of your entire data system (2 TB). In addition, 100 GB of new data is added every day. In the long term, this would mean a high storage load for your chosen storage medium. Full backups are therefore often used in combination with differential or incremental backups.
However, a decisive advantage of the full backup is the restore process.
If data is accidentally lost on Thursday evening, all your data can be restored from just a single backup file from Thursday. This shortens the duration of the restore process so that affected data is quickly ready for use again.
| Advantages full backup | Disadvantages full backup |
|
|
A differential backup is based on a full backup. This type of backup is always used when the difference to the last full backup is saved. This means that all data that has changed or been added since the last full backup is compiled in a backup file. Data changed from the previous day is overwritten to the current day:
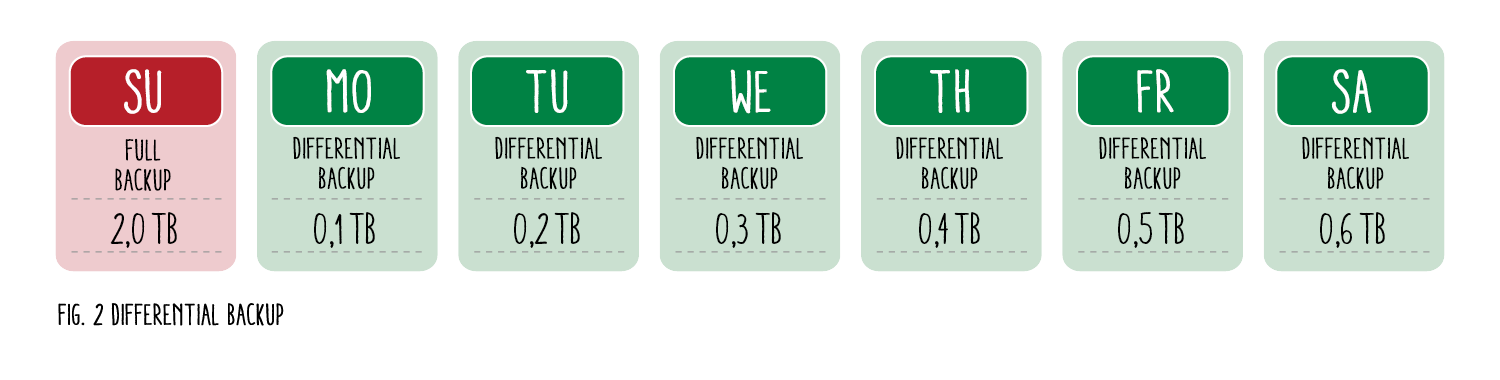
Imagine you make a full backup every Sunday and a differential backup from Monday to Saturday. Your entire file system takes up 2 TB and the new data added daily requires 100 GB. Due to a hardware defect on Wednesday evening, you will not be able to avoid a restore. To get your current data set back, you need to restore two backup files: 1. the full backup from Sunday (2 TB) and 2. the differential backup from Wednesday, i.e. a summary of all changes that took place on Monday, Tuesday and Wednesday (0.3 TB).
| Advantages differential backup | Disadvantages differential backup |
|
|
An incremental backup requires a full backup and only backs up the data that has changed since the last backup. In contrast to a differential backup, the changes from the previous day are not transferred to the current day. Because an incremental backup only backs up the data that has changed within a day, this type of backup uses the least storage space.
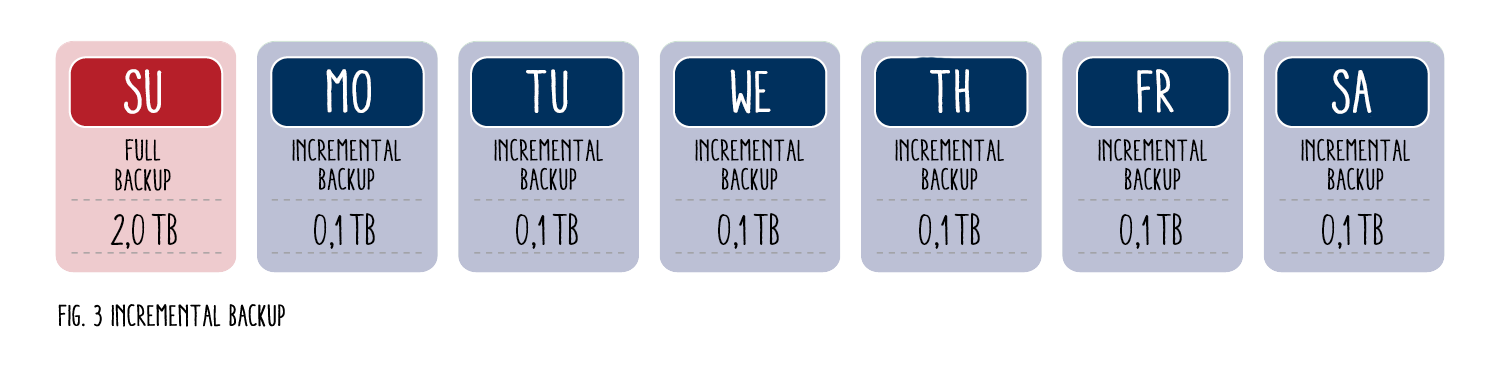
Let's assume that you want to perform a full backup every Sunday and an incremental backup from Monday to Saturday. Unfortunately, a cybercriminal uses phishing to gain access to your file system on Saturday morning. To get your data back, you need to restore the entire backup chain. This includes the full backup from Sunday and every single incremental backup from Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday. The restoration process is therefore much more complex than with the other two backup types.
| Advantages incremental backup | Disadvantages incremental backup |
|
|
In addition to the three file backup types, there is also the system backup. This refers not only to a specific file system or database, but to an entire system. This creates a system image of the installed operating system, including all system files, installed programmes and your own files. The result is a snapshot of all drives that are relevant for running the respective operating system. Instead of restoring all files individually, a completely operational system can be restored in the event of a serious software problem. This saves a lot of time compared to a new installation.
The 3-2-1 backup method serves as a first guide for creating a backup strategy. Multiple backup files should be distributed on different data carriers and stored separately from one another:
If your running server and backup server are affected by elemental damage or theft, the externally stored backup becomes a ray of hope. It therefore makes more than just sense to organise your strategy according to the 3-2-1 backup method.

Read our White Paper to find out how you can create a reliable safety net for your valuable data – and protect your business from the serious consequences of data loss.
You will find practical questions, a helpful checklist and real-world examples to help you make informed decisions about your data protection.
You agree to the processing of your data for the purpose of sending the newsletter. You can withdraw your consent at any time, for example by using the unsubscribe link in the newsletter. You can find detailed information on the processing of your personal data in our Privacy Policy under point 16.
If you have already discovered the right type of backup for you, you can follow the multi-generation backup principle – a popular backup method that can be used to optimise data backups. The aim is to carry out a complete data backup as efficiently as possible. And this is how it should work:
At the beginning of a data backup, a full backup is created and then daily backups – the so-called "son backups". The son backups can be either differential or incremental backups. At the end of the week, a complete backup, the "father backup", is performed. As this also contains all daily backups for the week, all previous backups (son backups) are deleted. After four weeks, four individual weekly father backups have accumulated, which are then removed by the "grandfather backup".
| Daily backup | son backup e.g. incremental or differential backup |
| Weekly backup | father backup replaces son backup with full backup at the end of a week |
| Monthly backup | grandfather backup replaces father backup with complete backup at the end of the month |
TIP: To be on the safe side, use different storage media for the different components of the multi-generation principle.
You have now developed an understanding of the different types of backup. In the next blog post, we would like to give you specific recommendations from our experts for a solid foundation. In particular, we will summarise helpful tips for selecting the right backup technology so that you can develop the right backup method for you.